The QueryChat Project, Mathematics of Machine Learning, New Tutorials | Issue 73
A weekly curated update on data science and engineering topics and resources.
This week's agenda:
Open Source of the Week - The QueryChat project
New learning resources - Introduction to agent skills, building pipeline parallelism for training AI models, adding interactivity to matplotlib with Marimo, introduction to Git and GitHub, NumPy crash course
Book of the week - Mathematics of Machine Learning by Tivadar Danka
The newsletter is also available on LinkedIn and Medium.
Are you interested in learning how to set up automated workflows with GitHub Actions? If so, please check out my course on LinkedIn Learning:
Open Source of the Week
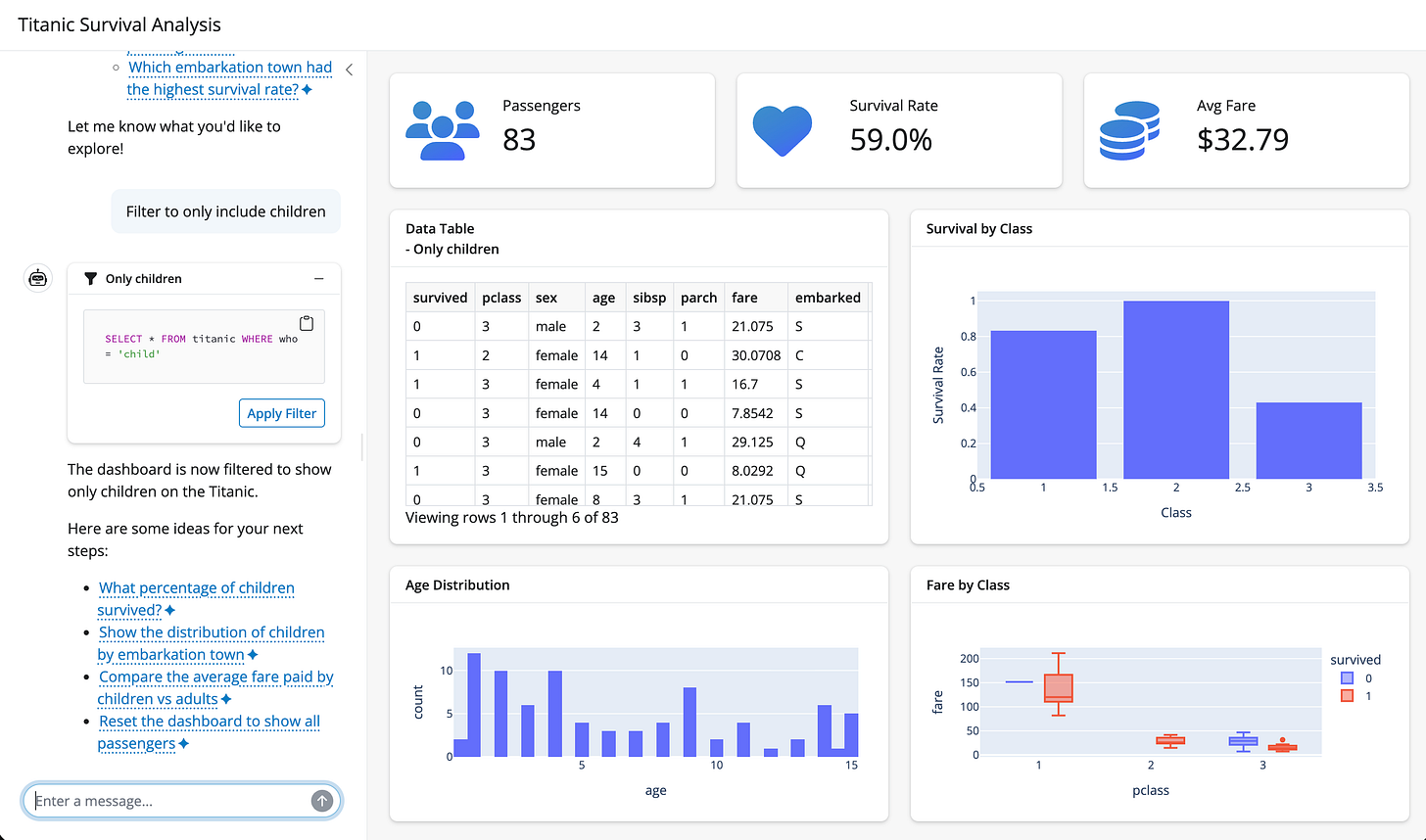
This week’s focus is on the QueryChat - an open source project from Posit that enables users to explore and analyze tabular data using natural language. Instead of relying on an LLM to directly summarize data, QueryChat translates user questions into executable SQL queries, runs them against the underlying data source, and returns both the results and the generated SQL. This approach improves correctness, transparency, and reproducibility when working with data, making it well-suited for analytics workflows in both Python and R.
Project repo: https://github.com/posit-dev/querychat
Key Features
Converts natural language questions into SQL queries that are executed against real data sources
Supports data frames and SQL backends (DuckDB by default, with extensibility to others)
Available for both Python and R, with first-class integration into analytical workflows
Designed for interactive applications, including Shiny (R and Python) and other web frameworks
Exposes generated SQL for inspection and auditing, reducing “black box” behavior
Allows customization of LLM providers and contextual metadata to improve query accuracy
If you want to learn more about the functionality of this library, here is a short tutorial by Veerle van Leemput for R:
And Python:
More details are available in the project documentation.
License: MIT
New Learning Resources
Here are some new learning resources that I came across this week.
Agents Skills
The following short tutorial by Alejandro AO provides an introduction to agent skills - the open standard for AI agent customization. The tutorial covers what skills are, how to use them, how to create one, and best practices.
Build Pipeline Parallelism from Scratch
The following tutorial by Kian Kyars focuses on building pipeline parallelism from scratch. Pipeline parallelism speeds up AI model training by splitting a massive model across multiple GPUs and processing data like an assembly line, ensuring no single device has to hold the entire model in memory.
Adding Interactivity to matplotlib with Marimo
The following tutorial by 👋 Vincent D. Warmerdam illustrates how to add interactivity to matplotlib graphs in Marimo notebooks. Super cool!
Introduction to Git and GitHub
The following tutorial by Federica Gazzelloni provides a beginner-friendly introduction to Git and GitHub.
NumPy Crash Course
The following tutorial by Tech with Tim provides an introduction to NumPy - Python core library for scientific computing.
Book of the Week
This week’s focus is on a data science book, Mathematics of Machine Learning by Tivadar Danka. The book dives into the core mathematical foundations beyond machine learning, including linear algebra, calculus, and probability theory.
What the book covers
Linear algebra fundamentals — vectors and vector spaces, norms and inner products, linear transformations, matrix equations, eigenvalues/eigenvectors, and advanced factorization techniques like SVD.
Vector spaces in practice — how to represent and manipulate mathematical objects in Python (NumPy) and understand their geometric structure.
Calculus essentials — limits, continuity, differentiation and integration, multivariable derivatives and gradients, and optimization techniques including gradient descent.
Probability theory — probability spaces, random variables and distributions, expected values, variance, and maximum likelihood estimation.
Connections to ML workflows — applying math concepts to problems like optimization for model training, understanding gradients and high-dimensional geometry, and interpreting probabilistic models.
Mathematical structure and logic — appendices on logic, set theory, and complex numbers to strengthen formal reasoning skills.
This book is ideal for aspiring machine learning engineers, data scientists, software developers, and researchers who want to deepen their mathematical understanding to confidently engage with advanced ML literature and practically implement algorithms; a basic background in algebra, Python, and introductory ML concepts will help you get the most out of it.
A hard copy is available for purchase on Amazon.
Have any questions? Please comment below!
See you next Saturday!
Thanks,
Rami